前言
本篇博客的写作背景基于近期实现的一个需求,该需求的大致内容如下:
- 基于全局的 Cesium 实例
- 全局 Cesium 实例中会存在多个点、线、面几何实体,代表一个
区域
- 每个
区域又可能由多个几何实体组成,例如道路就会包含 Polyline 及 Label,点则包含 Billboard 及 Label
由于 Cesium 实例是全局的,考虑到性能问题,主要是避免实体数量过多时,三维地球对浏览器的内存占用率过高,
所以对于点、线、面几何实体,采取编辑时使用 Entity,编辑完成/回显时转为 Primitive 进行渲染,节省内存并且提升渲染性能。
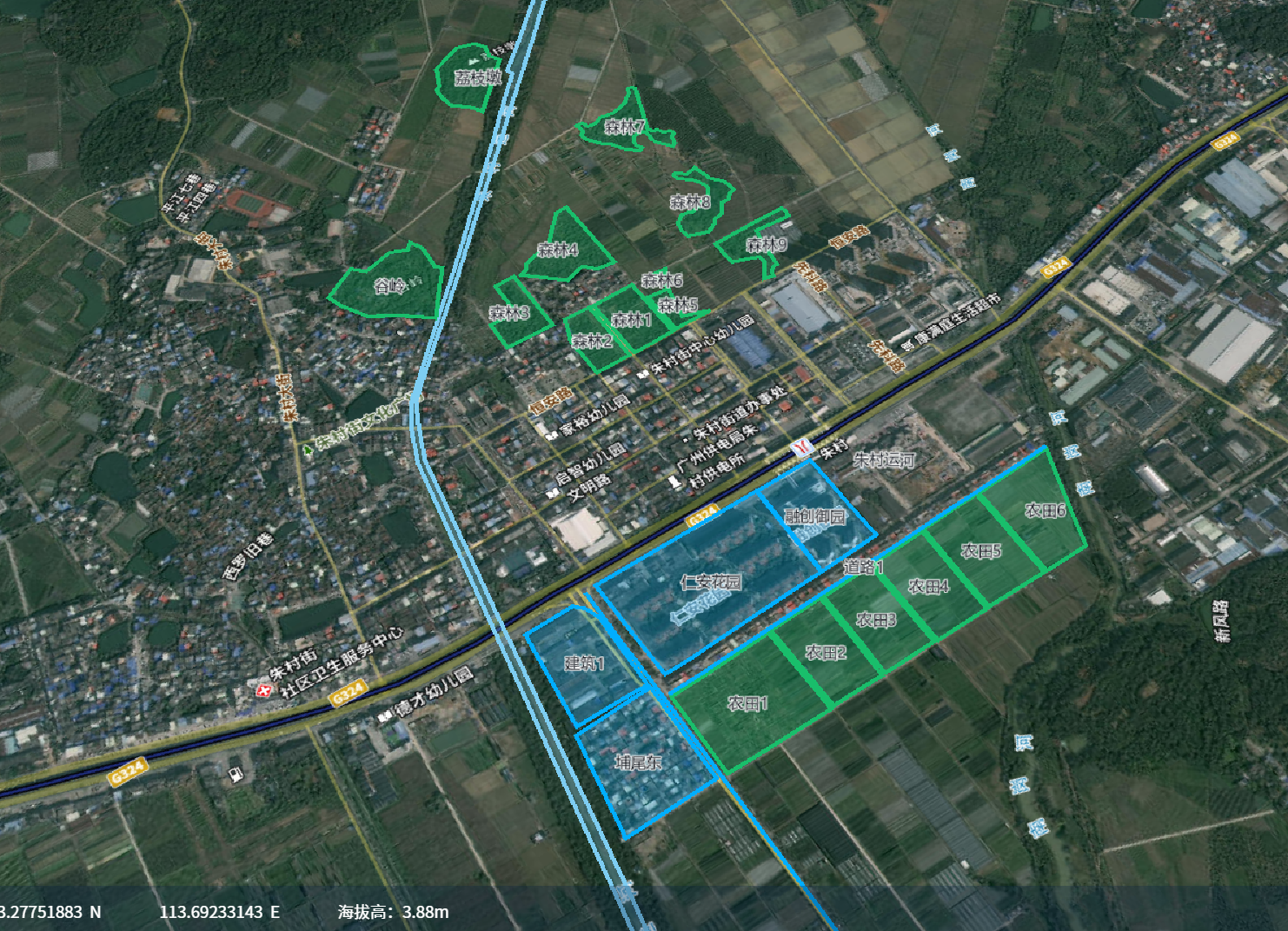
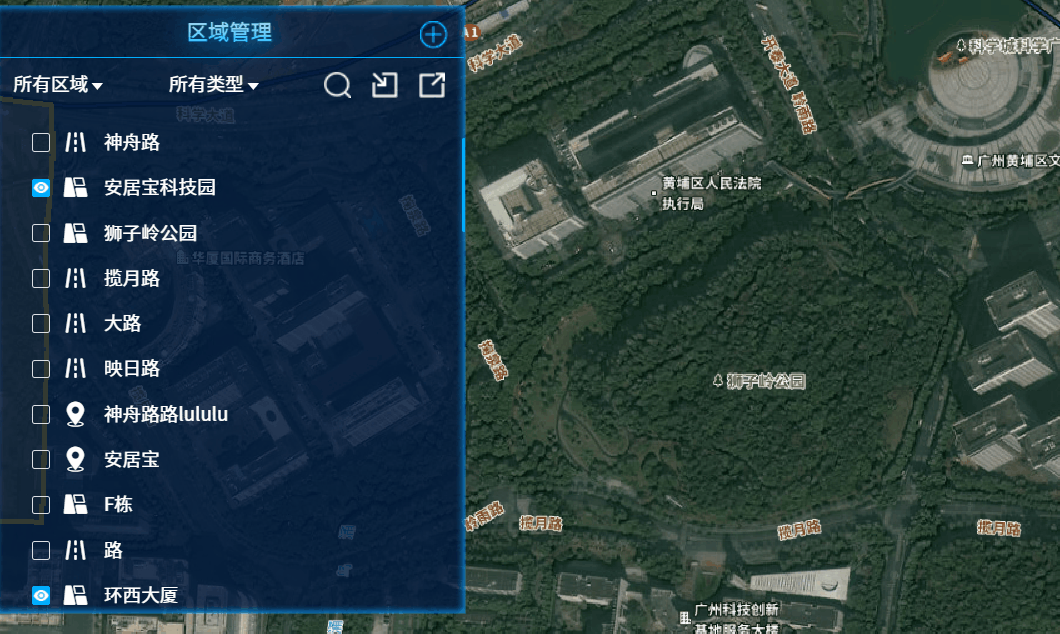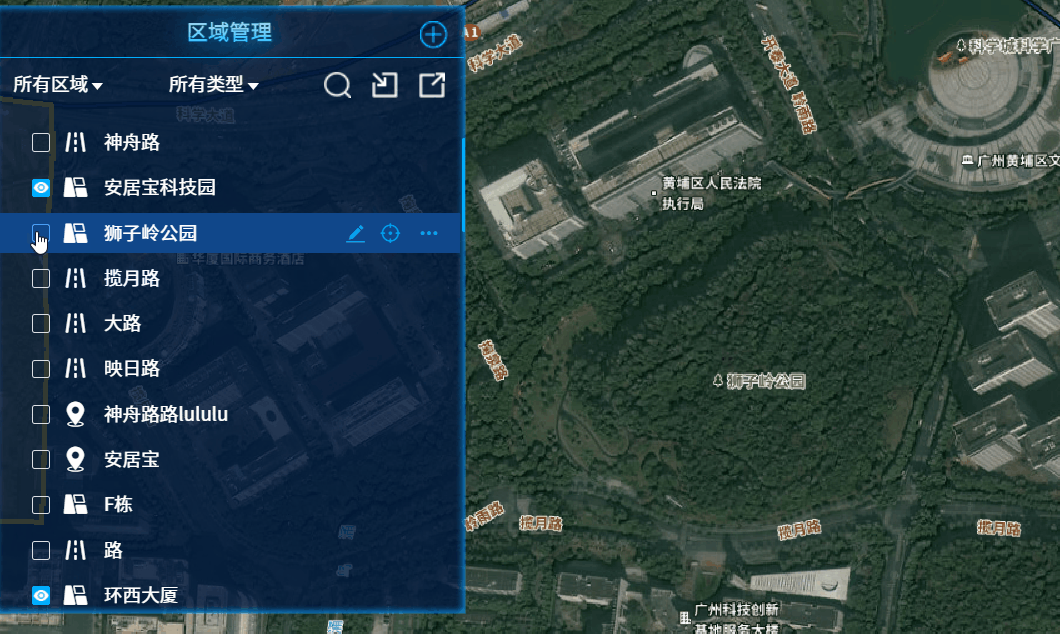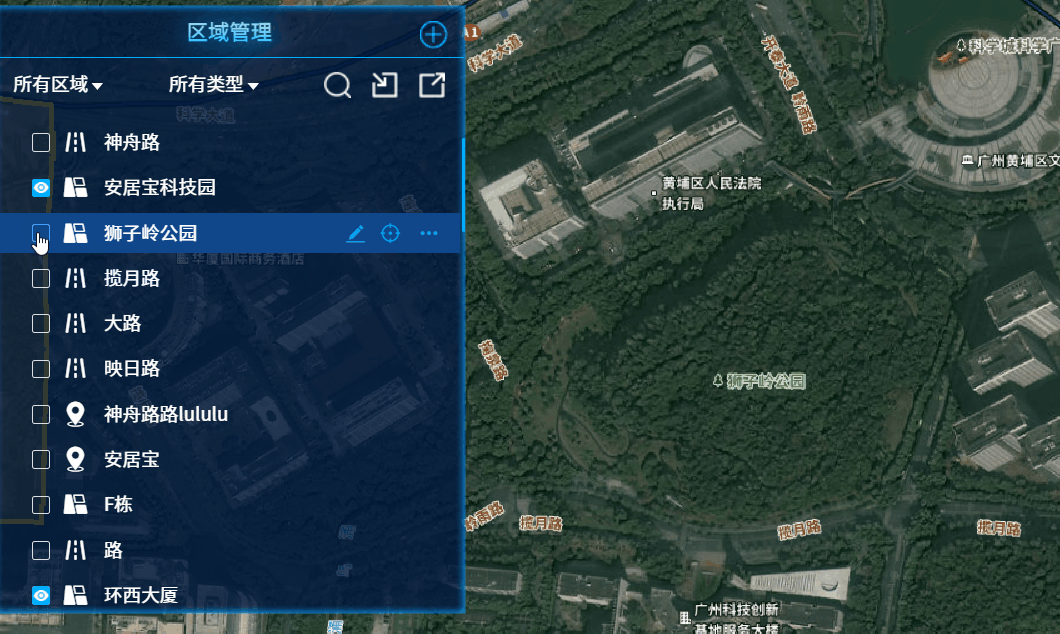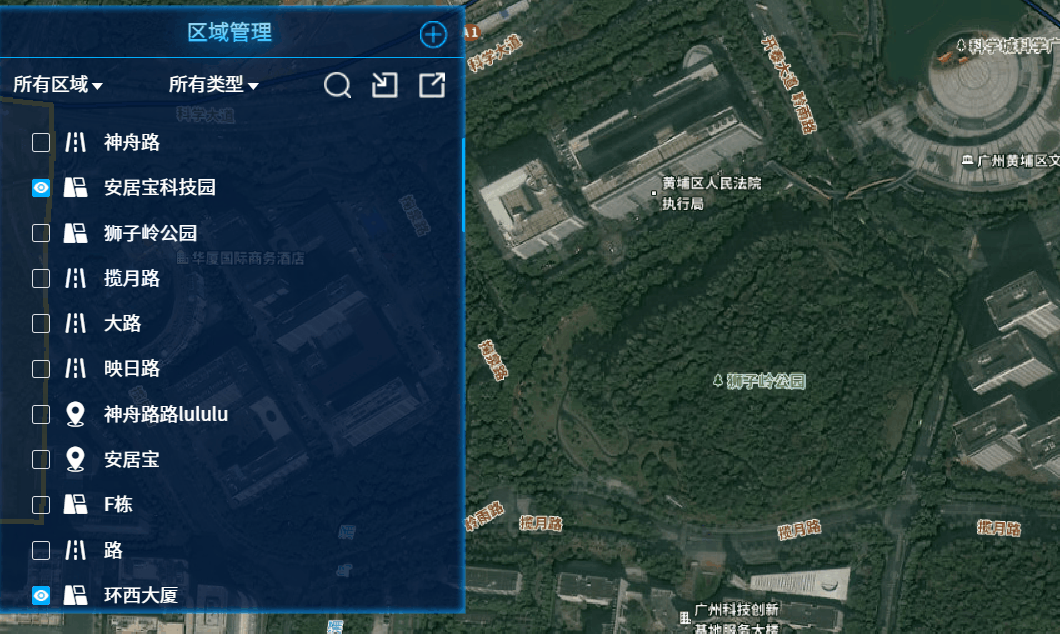
示例:部分几何图形
在示例图片中,可以看到部分这部分的区域都是由多边形和 label 组成的,每一个区域,都将会用一个类来表示。

示例:Entity 转换为 Primitive
点击保存后,Entity 便会转换成 Primitive

为什么是 Primitive
在日常开发中,出于方便,我们会使用 Cesium 提供的 Entity 类来对几何图形进行渲染和操作。
Entity 灵活易于使用,但 Entity 是一个高层次的概念,它可以自动处理许多与底层图形和几何形状相关的复杂性,例如纹理贴图、光照、碰撞检测等。
相对地,Primitive 则属于更低层次的概念,它通常用于描述一组简单的图形几何体,这跟我们的需求是吻合的。
更重要的是 Primitive 非常高效,因为它们使用了 GPU 硬件加速,且更接近 webgl 底层,可以轻松地绘制大量的几何体。
不过 Primitive 的缺点是不易于使用,上述提到的碰撞检测、 高级光照等渲染技术,通常需要手动处理,幸运的是,我们的需求并不涉及这些概念。
所以,通过 Primitive 渲染便成为了最合适的选择。
为什么是面向对象
根据业务需求,我们需要进行管理的单位是区域,而不是单个 Primitive,一个区域由多个 Primitive 组成。
所以,我们可以通过类,以区域为单位,对组成区域的所有有关联的 Primitive 进行封装:
- 方便可以通过区域 id 找到所有关联的 Primitive
- 可以将关联的 Primitive 看成一个整体,方便进行显隐、定位及删除操作
此外,类的 static 关键字可以简单地实现内存和数据的共享,这一点在稍后的篇章会提及。
声明「区域」类
声明 LocationPrimitive 类,代表一个区域。
我们假设,初始化一个区域所需要的几个条件分别为:经纬度(areaData)、颜色(areaColor)、名字(areaName)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
constructor(optoins, viewer) {
this._viewer = viewer
// 接口数据
this._options = optoins
// 所属 primitives
this._primitives = []
// 贴地 primitives
this._gPrimimitives = []
// primitive 的中心点位置,定位用
this._position = []
// id
this._id = ''
// 直接初始化
this.init()
}
/**
* 初始化类
*/
init() {
if (isEmpty(this._options.areaData)) {
console.error('初始化区域失败,区域位置数据为空')
}
if (isEmpty(this._options.areaColor)) {
console.error('初始化区域失败,颜色值为空')
}
if (isEmpty(this._options.areaName)) {
console.error('初始化区域失败,区域名称为空')
}
// 记录 id
this._id = this._options.id
// 经纬度转 cartesian 3
const position = JSON.parse(this._options.areaData)
const cartesian = position.map((p) => {
return Cesium.Cartesian3.fromDegrees(p[0], p[1], 0)
})
// 1区域 2道路 3点位
switch (this._options.areaType) {
case 1: {
cartesian.pop()
this._addGroundPolygon(cartesian)
this._addGroundPolyline(cartesian, true)
// label 位置,计算多边形中心
const boundingSphere = Cesium.BoundingSphere.fromPoints(cartesian)
const center = boundingSphere.center
this._position = center
this._addLabelPrimitive(center)
break
}
case 2: {
this._addGroundPolyline(cartesian, false)
let midpoint = null
if (cartesian.length === 2) {
midpoint = Cesium.Cartesian3.midpoint(cartesian[0], cartesian[1], new Cesium.Cartesian3())
} else if (cartesian.length % 2 !== 0) {
midpoint = cartesian[(cartesian.length - 1) / 2]
} else {
const index = cartesian.length / 2
midpoint = Cesium.Cartesian3.midpoint(
cartesian[index - 1],
cartesian[index],
new Cesium.Cartesian3()
)
}
this._position = midpoint
this._addLabelPrimitive(midpoint)
break
}
case 3: {
this._position = cartesian[0]
this._addPointPrimitive(cartesian[0])
this._addLabelPrimitive(cartesian[0], true)
break
}
}
// 默认显示
this.setDisplay(true)
}
_addGroundPolygon(){}
_addGroundPolyline(){}
_addLabelPrimitive(){}
_addPointPrimitive(){}
setDisplay(){}
}
|
创建贴地 Polygon
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// ...... //
/**
* 添加贴地多边形图元
* @param {Array} cartesian xyz 坐标
*/
_addGroundPolygon(cartesian) {
// 创建多边形几何描述
const polygonGeometry = new Cesium.PolygonGeometry({
polygonHierarchy: new Cesium.PolygonHierarchy(cartesian)
})
// 创建多边形的地面基元
const polygonPrimitive = new Cesium.GroundPrimitive({
show: false,
geometryInstances: new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
id: this._id,
geometry: polygonGeometry,
attributes: {
color: Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(
Cesium.Color.fromCssColorString(this._options.areaColor).withAlpha(0.26)
)
}
})
})
const primitive = this._viewer.scene.primitives.add(polygonPrimitive)
this._primitives.push(primitive)
}
}
|
创建贴地 Polyline
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// ...... //
/**
* 添加贴地多段线图元
* @param {Array} cartesian xyz 坐标
* @param {Boolean} loop 首尾相连
*/
_addGroundPolyline(cartesian, loop) {
// 创建折线 primitive
const polyline = new Cesium.GeometryInstance({
id: this._id,
geometry: new Cesium.GroundPolylineGeometry({
positions: cartesian,
loop: loop,
width: 4.0
}),
attributes: {
color: Cesium.ColorGeometryInstanceAttribute.fromColor(
Cesium.Color.fromCssColorString(this._options.areaColor)
)
}
})
const primitive = this._viewer.scene.groundPrimitives.add(
new Cesium.GroundPolylinePrimitive({
show: false,
geometryInstances: polyline,
appearance: new Cesium.polylineColorAppearance()
})
)
this._primitives.push(primitive)
this._gPrimimitives.push(primitive)
}
}
|
接下来,在实现创建 Label 和 Billboard 之前,有必要先介绍一下 static 关键字。
static 关键字
static 关键字常用于类中,它的作用是声明静态的方法或者属性。
而静态方法和属性是被类所拥有的,而不是类的实例,这就意味着,它们可以被该类的所有实例共享。
这是因为被 static 关键字修饰的方法和属性存在于栈内存中,而不是类的实例所在的堆内存,所以,静态属性的生命周期是从程序开始运行,一直到程序结束。
需要注意的是,被 static 声明的方法和属性,都不能通过 this 关键字访问。
在我们的需求中,我们需要创建的 label 以及 billboard 元素分别是基于 LabelCollection 以及 BillboardCollection 创建的。
相较于每个类中创建自己的 LabelCollection/BillboardCollection,然后每个 Collection 中只有一个元素,实际上是比较浪费的,Cesium 官方也不建议这么做。
所以我们可以通过共享的 Collection ,将每个类的 label/billboard 集中管理起来,达到优化的目的。
而至于怎么实现共享,靠的就是 static 关键字:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// 静态属性用于保存 billboard 和 label
static LocationBillboards = null
static LocationLabels = null
// ..略... //
}
|
我们声明了两个用于存放 collection 的静态变量,这两个变量会在类的第一次被初始化之前进行初始化
所以我们可以放心大胆地在构造函数中判断这两个属性是否已经被赋值,如果已经被初始化了,就跳过:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// 静态属性用于保存 billboard 和 label
static LocationBillboards = null
static LocationLabels = null
constructor(optoins, viewer) {
this._viewer = viewer
// 接口数据
this._options = optoins
// 所属 primitives
this._primitives = []
// 贴地 primitives
this._gPrimimitives = []
// primitive 的中心点位置,定位用
this._position = []
// id
this._id = ''
// 直接初始化
this._initStaticResource()
console.log('new object')
this.init()
}
/** 初始化静态资源 */
_initStaticResource() {
if (isEmpty(LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards)) {
console.log('init billboard')
LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards = new Cesium.BillboardCollection({ scene: this._viewer.scene })
this._viewer.scene.primitives.add(LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards)
}
if (isEmpty(LocationPrimitive.LocationLabels)) {
console.log('init label')
LocationPrimitive.LocationLabels = new Cesium.LabelCollection({ scene: this._viewer.scene })
this._viewer.scene.primitives.add(LocationPrimitive.LocationLabels)
}
}
}
|
这个时候即使你遍历 10 次,new LocationPrimitive 对象,然后在构造函数以及初始化静态资源方法中进行打印,就可以观察到 new object 被打印了 10 次,但是 init billboard 和 init label 只会被打印一次。
通过这个观察,就可以判断出 static 数据确实是被共享的。
完善区域类
接下来,对区域类进行完善,实现一些提供给外部调用的方法,就大功告成了。
显隐切换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// ...
// 切换显隐
setDisplay(show) {
this._primitives.forEach((p) => {
p.show = show
})
const billboard = this._getTargetBillboard()
billboard && (billboard.show = show)
const label = this._getTargetLabel()
label && (label.show = show)
}
// 根据 id 从静态 billboard collection 中找到目标 billboard
_getTargetBillboard() {
return LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards._billboards.filter((b) => b).find((b) => b.id === this._id)
}
// 根据 id 从静态 label collection 中找到目标 label
_getTargetLabel() {
return LocationPrimitive.LocationLabels._lassbels.filter((l) => l).find((l) => l.id === this._id)
}
}
|

定位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// ...
// 定位
located() {
this._viewer.camera.flyTo({
destination: this._position,
orientation: {
heading: Cesium.Math.toRadians(0),
pitch: Cesium.Math.toRadians(-90),
roll: 0.0
},
duration: 1
})
}
}
|
释放资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
export default class LocationPrimitive {
// ...
// 从地图上移除 primitive & 释放显存
free() {
// 移除一般图元
this._primitives.forEach((p) => {
p.removeAll && p.removeAll()
this._viewer.scene.primitives.remove(p)
})
// 移除贴地图元
this._gPrimimitives.forEach((p) => {
this._viewer.scene.groundPrimitives.remove(p)
})
// 移除 billboard 和 label
const billboard = this._getTargetBillboard()
const label = this._getTargetLabel()
if (billboard) LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards.remove(billboard)
if (label) Locat
ionPrimitive.LocationLabels.remove(label)
}
// 释放静态资源,只会被调用一次
freeStaticResource() {
if (LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards) LocationPrimitive.LocationBillboards = null
if (LocationPrimitive.LocationLabels) LocationPrimitive.LocationLabels = null
}
}
|
提供静态工具类
在现代的前端框架中,一般来说操作全局的数据都不太方便,所以我们可以提供一个纯静态的工具类,供所有组件使用。
纯静态工具类中,所有属性和方法都是静态的,但是这个类会随着程序的启动而直接初始化,所以在任意组件中都可以直接使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
// 纯静态工具类,收集所有全局的 primitive
export default class PrimitivesCollection {
// 保存所有实例化的数据
static data = []
/**
* 将接口数据初始化成 primitives
* @param {Array} data
* @param {Object} viewer
*/
static rawDataToPrimitives(data, viewer) {
if (data && data.length > 0) {
data.forEach((d) => {
const primitiveInstance = new LocationPrimitive(d, viewer)
PrimitivesCollection.data.push(primitiveInstance)
})
}
}
/**
* 根据 id 定位区域
* @param {String} id
*/
static locatedRegion(id) {
const instance = PrimitivesCollection.getTargetById(id)
if (instance) {
instance.located()
}
}
/**
* 切换指定区域的显隐
* @param {String} id
* @param {Boolean} show 是否显示
*/
static toggleRegionDisplay(id, show) {
const instance = PrimitivesCollection.getTargetById(id)
if (instance) {
instance.setDisplay(show)
}
}
/**
* 销毁图元释放内存
* @param {String} id
*/
static remove(id) {
const needClear = PrimitivesCollection.getTargetById(id)
if (needClear) {
needClear.free()
PrimitivesCollection.data = PrimitivesCollection.data.filter((d) => d.id !== id)
}
}
// 根据 id 获取目标
static getTargetById(id) {
return PrimitivesCollection.data.find((d) => d.id === id)
}
// 完全清理全局数据
static clearAll() {
// 获取全局 viewer
const viewer = getViewer()
PrimitivesCollection.data.forEach((p) => p.free())
PrimitivesCollection.data.forEach((p) => p.freeStatic())
PrimitivesCollection.data.length = 0
}
}
|
对数据进行最细粒度更新
由于有了类去管理数据,我们在进行数据更新时,就可以对现有的数据以及新数据进行 diff 比对,务求做到最细粒度的更新。
例如,用户对数据进行刷新,其中有一个区域被删除,两个区域被修改,新增三个区域,那么,我们只需要把这些改动的部分找出来,对其进行操作,而不需要对所有已存在的区域进行操作,减少操作次数,以达到优化性能的目的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
// 纯静态工具类,收集所有全局的 primitive
export default class PrimitivesCollection {
// 保存所有实例化的数据
static data = []
/**
* 将新旧数据进行 diff 对比差异,最小粒度更新地图上的数据
* 1、如果其他用户删除了某个区域,当前用户刷新列表时,这个删除动作应该同步到当前用户
* 2、如果其他用户新增了区域,当前用户刷新列表时,这个新增动作应该同步到当前用户
* 3、如果其他用户修改了区域的颜色或者名称,用户刷新列表时,这个修改动作应该同步到当前用户
* @param {Array} newData 新的数据(接口数据非对象数据)
*/
static updateMapByDiff(newData) {
const viewer = getViewer()
// 将数组转为 map 来实现后续的快速查找,主要是为了节省遍历操作
const oldDataMap = PrimitivesCollection.data.reduce((data, item) => ((data[item.id] = item), data), {})
const newDataMap = newData.reduce((data, item) => ((data[item.id] = item), data), {})
// 将 map 的 key 装进 set 中,也是为了节省遍历操作
const oldIds = new Set(Object.keys(oldDataMap))
const newIds = new Set(Object.keys(newDataMap))
// 将 id 过滤出来
const addedIds = Array.from(newIds).filter((id) => !oldIds.has(id))
const removeIds = Array.from(oldIds).filter((id) => !newIds.has(id))
// 删除不再存在的项
removeIds.forEach((id) => PrimitivesCollection.remove(id))
// 新增的数据 new 成实例
for (let addedId in addedIds) {
const item = newDataMap[addedId]
if (item) {
const primitiveInstance = new LocationPrimitive(item.viewer)
PrimitivesCollection.data.push(primitiveInstance)
}
}
// 获取交集
const intersection = Array.from(oldIds).filter((id) => newIds.has(id))
// 更新存在于新旧数据中,但有变化的项
for (let intersectingId in intersection) {
const oldData = oldDataMap[intersectingId]
const newData = newDataMap[intersectingId]
if (oldData.options.areaName !== newData.areaName || oldData.options.areaColor !== newData.areaColor) {
PrimitivesCollection.remove(intersectingId)
const primitiveInstance = new LocationPrimitive(newData, viewer)
PrimitivesCollection.data.push(primitiveInstance)
}
}
}
}
|
总结
近些年在使用 JavaScript 进行开发的开发者们,大多数是在成熟的前端框架的基础上进行开发,对 JavaScript 本身的面向对象特性了解或者使用是比较少的。
可能是得益于 TypeScript 的出现,这种情况似乎有所改变,一些开发者在使用 TS 编码时可能会优先考虑面向对象,我就是其中之一。
所以当又回到 JavaScript 的时候,只要利用这些成熟的编码模式对代码进行设计和封装,就能轻松写出优雅的代码。
(完)