前言
这篇博客主要介绍在相对复杂一点的业务场景下,前端如何通过 Promise 以及 async/await 语法,在一个动作/事件中同时处理多个异步请求,使代码更加简洁。
本次介绍的场景主要有两个:
- 多个请求之间有依赖关系,一个请求可能依赖上一个请求返回的结果或需要按顺序调用
- 多个请求之间没有依赖关系
场景一:请求间有依赖关系
Promise 回调地狱
大多数刚刚入门的前端,肯定听过这样一句话:Promise 解决了传统异步请求的回调地狱问题。
但真的是这样吗,看看下面的例子:
在当前组件初始化的时候,顺序调用三个请求:getUser => getPost => getCommons,并假设每个请求依赖前一个请求的结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
mounted(){
this.init('1')
},
data(){
return{
posts:[]
}
},
methods:{
/**
* fake API 来自:https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/
*/
getUser(id){
return axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/' + id)
},
getPost(id){
return axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/' + id)
},
getCommons(id){
return axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/' + id + '/comments')
},
//初始化方法
init(id){
this.getUser(id).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
this.getPost(id).then(res1=>{
console.log(res1.data)
this.getCommons(id).then(res2=>{
console.log(res2.data)
})
})
})
}
}
}
</script>
|
注意看初始化方法init(),根据需求我们按顺序调用了三个接口,在异步请求返回时,将返回结果打印出来,这个时候。可怕的回调地狱金字塔就出现了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<script>
methods:{
//初始化方法
init(id){
//请求一
this.getUser(id).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
//请求二
this.getPost(id).then(res1=>{
console.log(res1.data)
//请求三
this.getCommons(id).then(res2=>{
console.log(res2.data)
})
})
})
}
}
}
</script>
|
Promise 的链式调用
所以,在以上的场景下,如果不按照规范来写异步代码,即便使用了 Promise,还是会出现回调地狱。
那么正确的使用方法应该是怎样的呢?
其实也很简单,我们在 .then()里面不要直接调用下一个请求,而是return出去,然后再通过.then()来获取他的返回结果就可以了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
<script>
methods:{
//初始化方法
init(id){
//请求一
this.getUser(id).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
//请求二
return this.getPost(id)
}).then(res1=>{
console.log(res1.data)
//请求三
return this.getCommons(id)
}).then(res2=>{
console.log(res2.data)
}).catch(err=>{
console.log(err)
})
}
}
</script>
|
这样做,就避免了请求过多时产生的金字塔形的嵌套,而且还可以通过.catch()的穿透性来捕获错误,使代码更加简洁。
场景二:请求间没有依赖关系
场景描述:当用户点击时打印加载中,同时调用三个接口:getUser 、 getPost、 getCommons,接口之间没有依赖关系,当三个接口返回成功后,打印加载完毕。
Promise.all() + async/await 语法
Promise.all()接受一个 Promise 对象数组作为参数,当数组中所有 Promise 对象都返回成功的话,Promise.all()会返回一个状态为兑现的 Promise 对象,否则返回一个状态为拒绝的 Promise 对象。
async/await 语法使用方法请参考MDN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<script>
methods:{
//初始化方法
async init(id){
console.log('加载中...')
const getUser = this.getUser(id) //请求一
const getPost = this.getPost(id) //请求二
const getCommons = this.getCommons(id) //请求三
//用 Promise.all() 同时发送三个请求
try{
const result = await Promise.all([getUser,getPost,getCommons])
console.log(result)
console.log('加载完成')
}catch (err){
console.log(err)
}
}
}
</script>
|
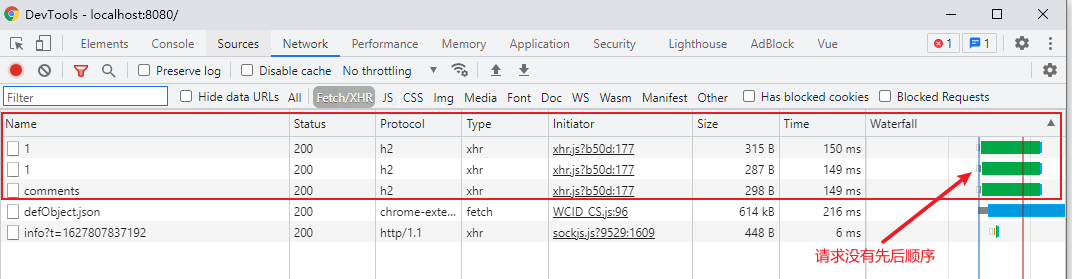
将三个请求作为参数传入 Promise.all(),方法,并利用 try … catch 捕获可能发生的错误,最终效果如下图:

可以发现由于三个请求并没有相互依赖关系,所以在同一时间发送可以减少异步请求的等待时间,最后获取到所有结果。
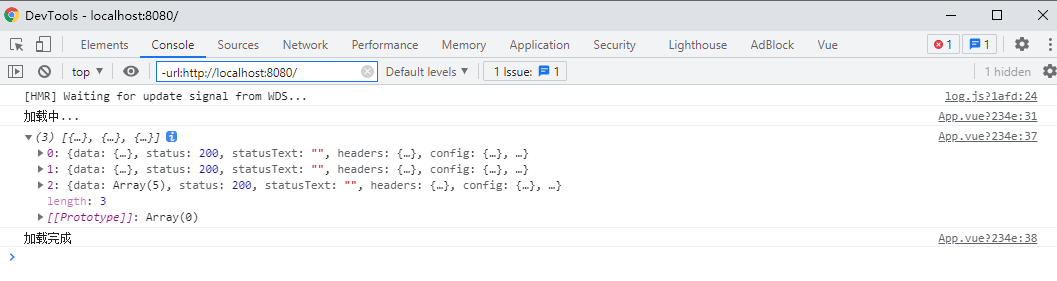
Promise.all()方法返回的是一个数组,里面包含了我们三个请求对应的结果:

这个数组中所包含的的结果,跟我们参数传递的数组中的 Promise 对象是一一对应的,所以我们可以根据 result 数组的下标,获取到每个请求对应的数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
<script>
data(){
return{
post:{},
user:{},
commons:[]
}
},
methods:{
//初始化方法
async init(id){
console.log('加载中...')
const getUser = this.getUser(id) //请求一
const getPost = this.getPost(id) //请求二
const getCommons = this.getCommons(id) //请求三
//用 Promise.all() 同时发送三个请求
try{
const result = await Promise.all([getUser,getPost,getCommons])
//装载对应的数据
this.user = result[0].data
this.post = result[1].data
this.commons = result[2].data
console.log('加载完成')
}catch (err){
console.log(err)
}
}
}
</script>
|
总结
ES6+ 为开发者提供了很多非常好用的 API,正确地使用他们可以写出更加简洁优雅的代码。